Understanding Competitive Analysis kicks off the ultimate business showdown, shedding light on the strategic maneuvers that dominate the market landscape. Get ready to dive deep into the realms of business rivalry and market dominance!
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the ins and outs of competitive analysis, from unraveling the importance of assessing competitors to deciphering the key metrics that drive business success.
Overview of Competitive Analysis
Competitive analysis plays a crucial role in shaping successful business strategies by providing valuable insights into the market landscape and the competitive environment. It helps businesses understand their competitors’ strengths and weaknesses, identify opportunities for growth, and anticipate potential threats.
Importance of Competitive Analysis
Competitive analysis is essential for businesses to stay ahead of the competition and make informed decisions. By analyzing competitors’ strategies, products, pricing, and marketing tactics, companies can identify gaps in the market and develop unique selling propositions to differentiate themselves.
Understanding the Market Landscape
By conducting competitive analysis, businesses gain a better understanding of the market landscape, including key players, market trends, customer preferences, and industry dynamics. This information helps in developing targeted marketing campaigns, product innovations, and pricing strategies to meet customer needs effectively.
Examples of Industries where Competitive Analysis is Crucial
Competitive analysis is especially crucial in industries with intense competition and rapid technological advancements, such as the technology sector, retail industry, automotive industry, and telecommunications sector. Companies in these industries often rely on competitive analysis to stay competitive, drive innovation, and adapt to changing market conditions.
Types of Competitive Analysis: Understanding Competitive Analysis
Competitive analysis involves evaluating the strengths and weaknesses of competitors to identify opportunities and threats in the market. There are different types of competitive analysis that companies use to stay ahead of the competition.
Direct vs. Indirect Competitors, Understanding Competitive Analysis
Direct competitors are businesses that offer similar products or services to the same target market. They are the most obvious competitors and often have a direct impact on your sales and market share. Indirect competitors, on the other hand, may offer different products or services but still compete for the same consumer dollars. Understanding both types of competitors is crucial for developing a comprehensive competitive strategy.
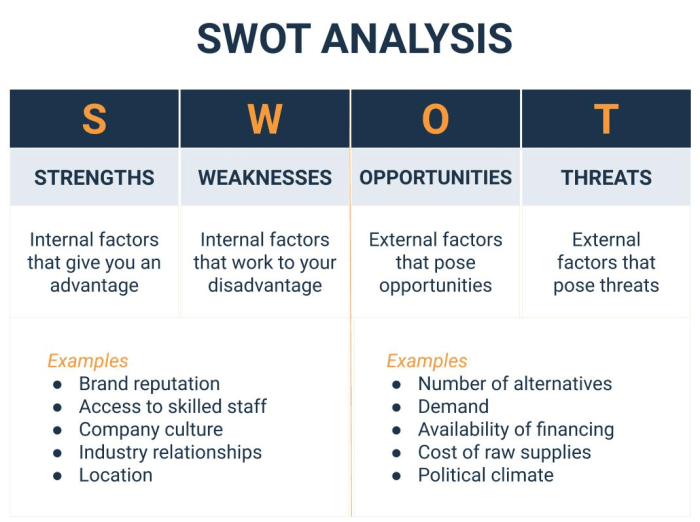
Significance of SWOT Analysis
SWOT analysis is a strategic planning tool that helps businesses identify their internal strengths and weaknesses, as well as external opportunities and threats. In competitive analysis, SWOT analysis is used to assess how a company stacks up against its competitors. By identifying key areas of strength and areas that need improvement, businesses can develop strategies to capitalize on opportunities and mitigate threats in the market.
Benchmarking for Competitive Performance
Benchmarking involves comparing your company’s performance metrics to those of your competitors to identify areas where you excel and areas where you need to improve. By benchmarking against industry leaders or direct competitors, businesses can set performance goals, track progress, and make informed decisions to stay competitive in the market.
Conducting Competitive Analysis
When conducting competitive analysis, it is essential to follow a structured approach to gather valuable insights that can help in making informed business decisions.
Steps Involved in Conducting Competitive Analysis
- Identify the industry or market in which your business operates.
- Define the scope of your analysis, including the products or services to be compared.
- Gather information about your competitors, such as their market share, pricing strategies, and target audience.
- Analyze the strengths and weaknesses of each competitor to identify potential threats and opportunities.
- Develop a competitive matrix to compare key metrics and performance indicators across competitors.
- Draw insights from the analysis to refine your business strategies and gain a competitive advantage.
Tools and Techniques Used for Competitive Analysis
- SWOT Analysis: Identifying strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats of your competitors.
- Porter’s Five Forces: Analyzing competitive forces within an industry that can impact profitability.
- Market Research: Conducting surveys, focus groups, and interviews to gather data on competitors.
- Competitor Benchmarking: Comparing your business performance with that of key competitors.
Identifying Key Competitors for Analysis
- Look for companies offering similar products or services in the same target market.
- Consider both direct competitors (offering identical products) and indirect competitors (serving similar needs).
- Examine market leaders and emerging players that could pose a threat to your business in the future.
- Monitor industry trends and news to stay updated on new entrants and disruptors in the market.
Competitive Analysis Metrics
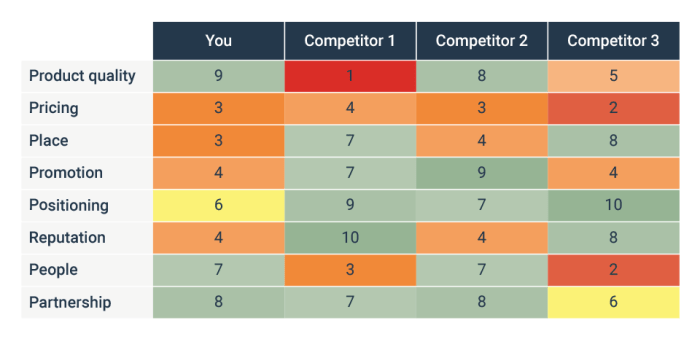
When it comes to measuring competitive performance, there are several common metrics that are used in competitive analysis. These metrics help businesses understand how they stack up against their competitors and identify areas for improvement.
Qualitative vs Quantitative Metrics
Qualitative metrics in competitive analysis involve subjective assessments and observations that are not easily quantifiable. These can include factors such as brand reputation, customer satisfaction, and product quality. On the other hand, quantitative metrics are measurable and typically involve numerical data such as market share, revenue growth, and customer acquisition cost.
KPIs for Measuring Competitive Performance
- Market Share: This metric measures the percentage of total sales in an industry that a company holds. It helps businesses understand their position relative to competitors.
- Customer Churn Rate: This KPI indicates the percentage of customers who stop using a company’s products or services over a certain period. A high churn rate could signal issues with customer satisfaction or competitive offerings.
- Net Promoter Score (NPS): NPS measures customer loyalty and satisfaction by asking customers how likely they are to recommend a company to others. A high NPS indicates strong customer advocacy.
- Price Competitiveness: This metric compares a company’s pricing strategy to that of competitors. It helps businesses determine if they are offering competitive prices in the market.